Big Data and Fast Data are solving IT challenges long thought to be unreachable. Think of Big Data as an amount of data so large and complex that traditional database management tools are useless. Fast Data, on the other hand, is when that data is put into motion to quickly gather and mine structured and unstructured data so that action can be taken.
Together, Big Data and Fast Data are opening up exciting opportunities. At the same time, this "Big and Fast" wave is pushing the boundaries of the technologies and frameworks we've tended to use for awhile.
It's not that easy -- and moreover all that cheap -- to scale a single-server relational database in order to keep up with massively growing data volumes. Plus, not every company can afford to upgrade from one powerful, expensive mainframe to another whenever it's needed.
What's worse, even if your budget is unlimited, the hardware is not -- at some point in time you might not be able to find a server that could fit and process all the data on its own.
Luckily, the software market embraced the challenge and outfitted us with a variety of distributed storage and computational platforms that both store and process the data in a distributed fashion supporting a horizontal scalability principle.
GridGain In-Memory Data Fabric is one of the pioneers in this area. It's a distributed in-memory data fabric, built on top of open source Apache Ignite In-Memory Data, that can store and process data across a cluster of machines -- boosting the performance of your applications tens, hundreds or thousands of times.
With this blog post, we kickoff a series of articles about GridGain cluster deployment and utilization in cloud environment’s like Amazon Web Services (AWS). From this particular article, you'll learn how to deploy a cluster on AWS in the fastest way possible (five minutes) using AWS Marketplace.
Installing GridGain From AWS Marketplace
It's obvious that GridGain Enterprise Edition can be deployed on AWS without any interaction at all with the AWS Marketplace. However, sometimes we want it to be a burden of a cloud provider rather than us and this is when marketplaces join the game.
Following the provided instructions, let's go to AWS Marketplace and type in GridGain in the search box:
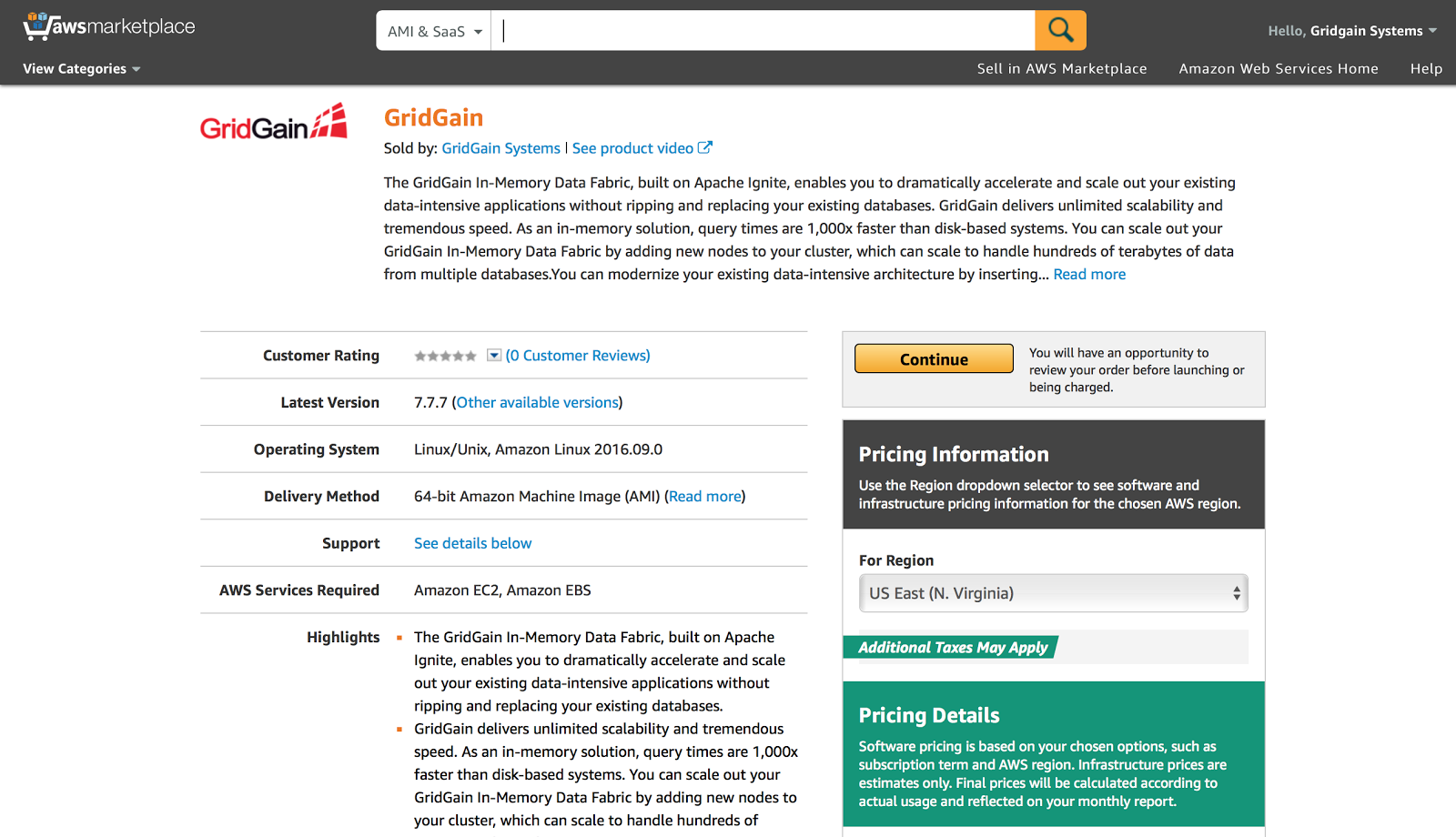
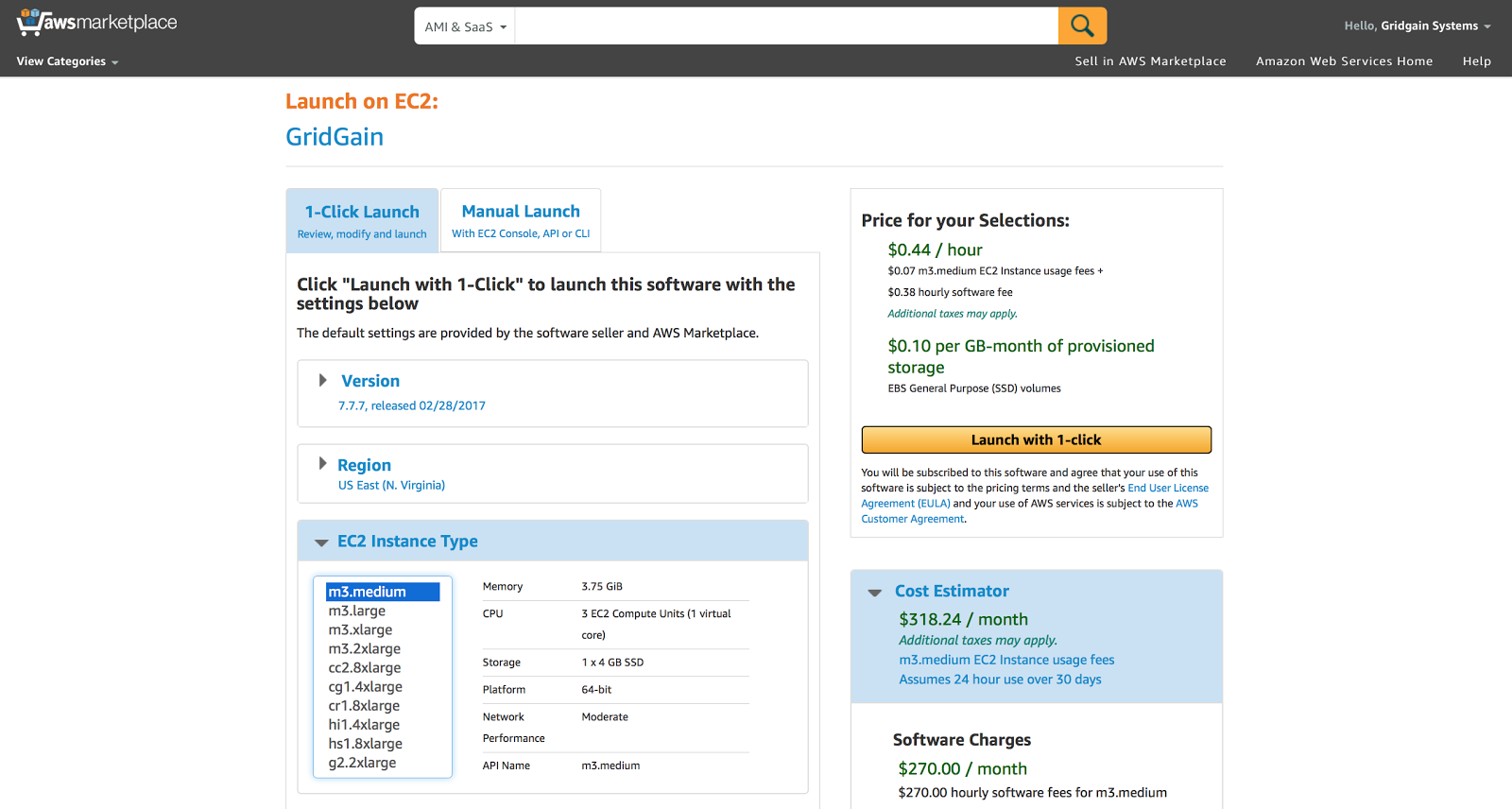
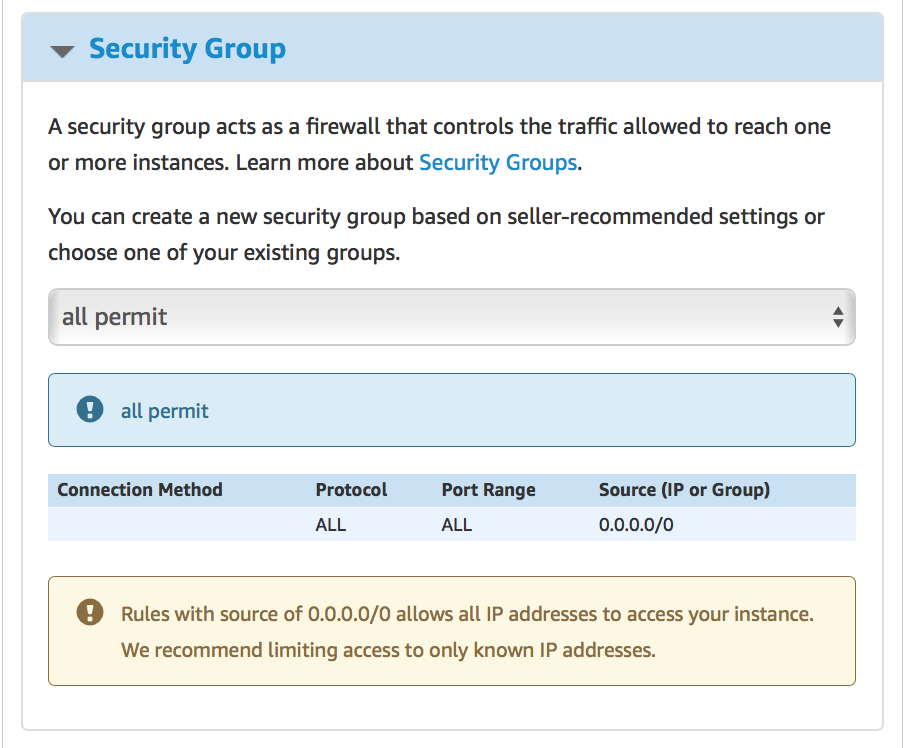
Alter the rest of the parameters on this screen if required and move to the next stage clicking on “Launch with 1-Click” button:
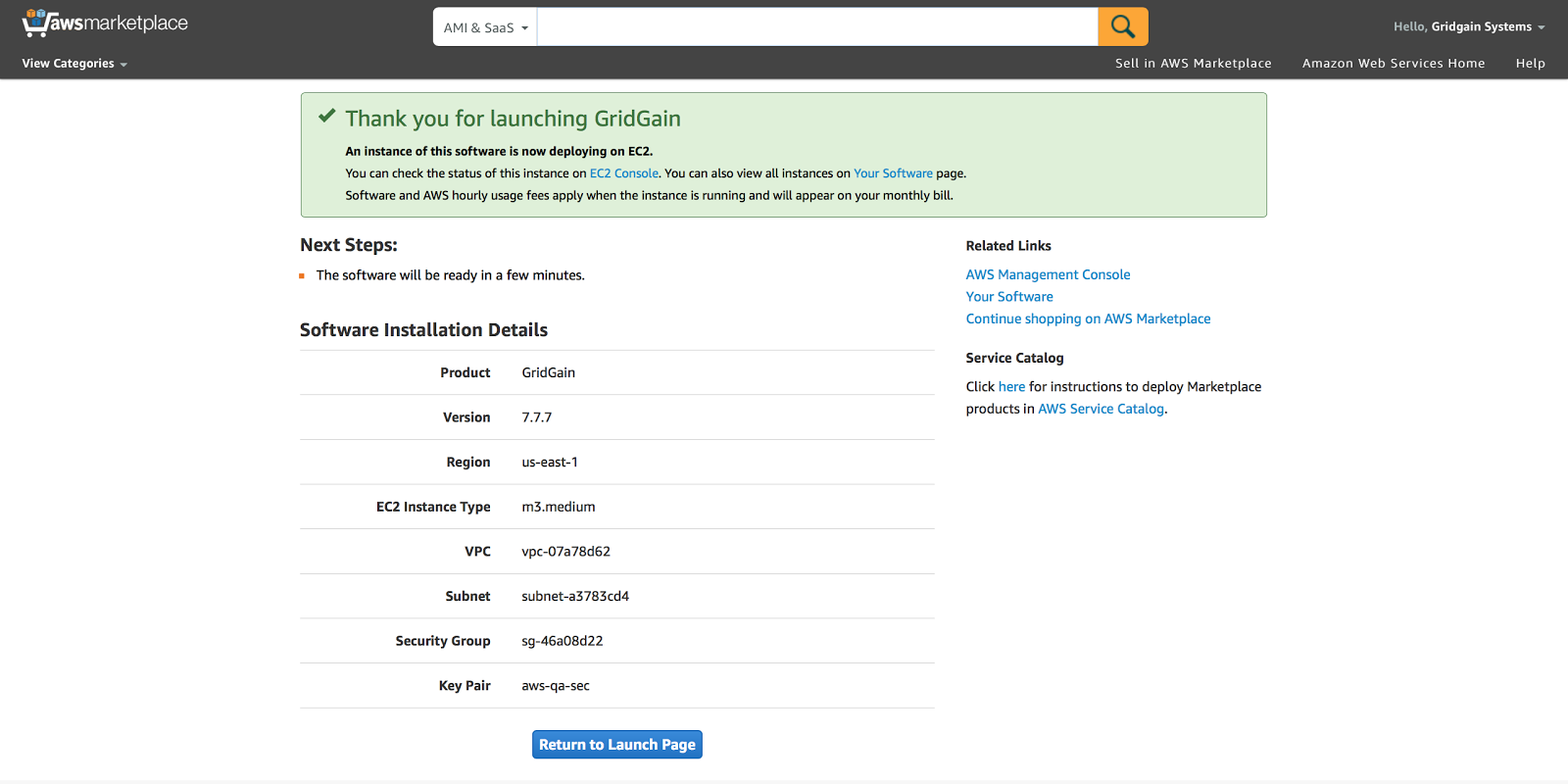
Go to E2C Console and make sure the EC2 instance is ready for usage:
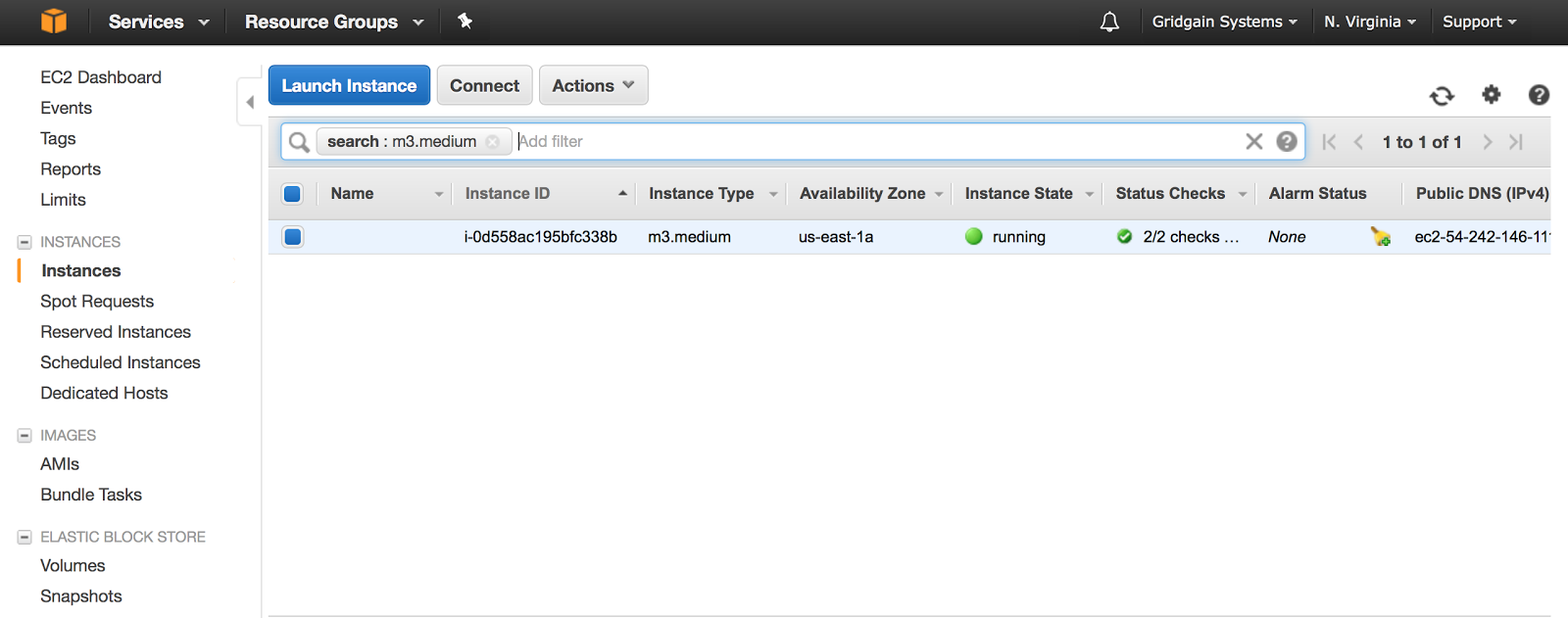
Launching GridGain Cluster
As the next step let's use SSH to connect to the running EC2 instance and launch a GridGain cluster there. For instance, this one of possible connection strings that encompass a reference to the secret key and EC2 instance public DNS name:
ssh -i "dmagda.pem" ec2-user@ec2-54-82-240-125.compute-1.amazonaws.com
Once connected, set up several required environment variables as shown below. Your JDK and GridGain versions might be different, so make sure you specified the correct ones:
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk.x86_64
export IGNITE_HOME=/usr/local/bin/gridgain/gridgain-enterprise-fabric-7.7.7
export GRIDGAIN_HOME=${IGNITE_HOME}
Go to GRIDGAIN_HOME dir and execute ignite-amazonaws-example.sh directly from there. The script will launch the first GridGain node:
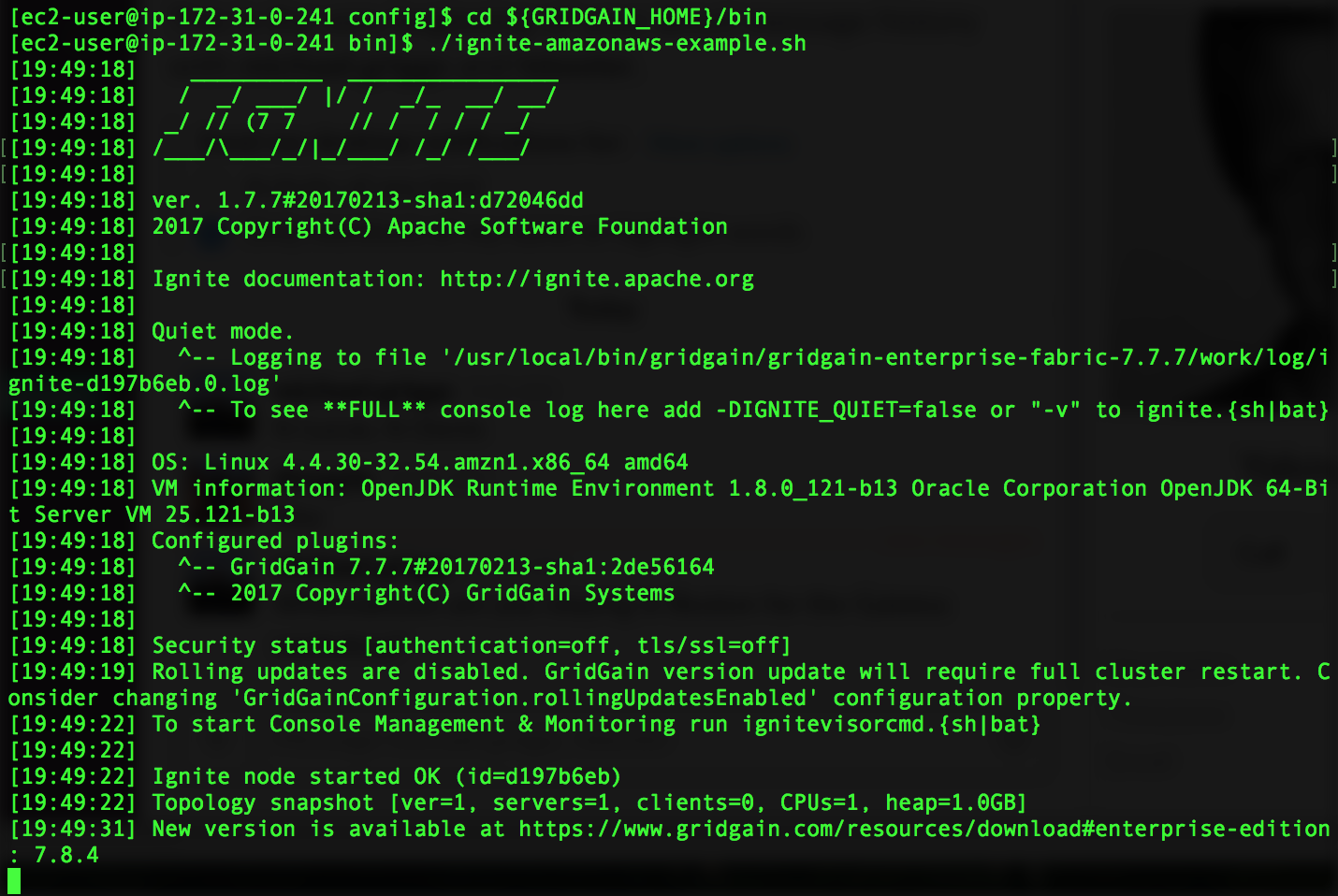
Move this GridGain node process to the background by pressing Crtl-Z keys and executing bg command right after that. Start the second node using the similar script:
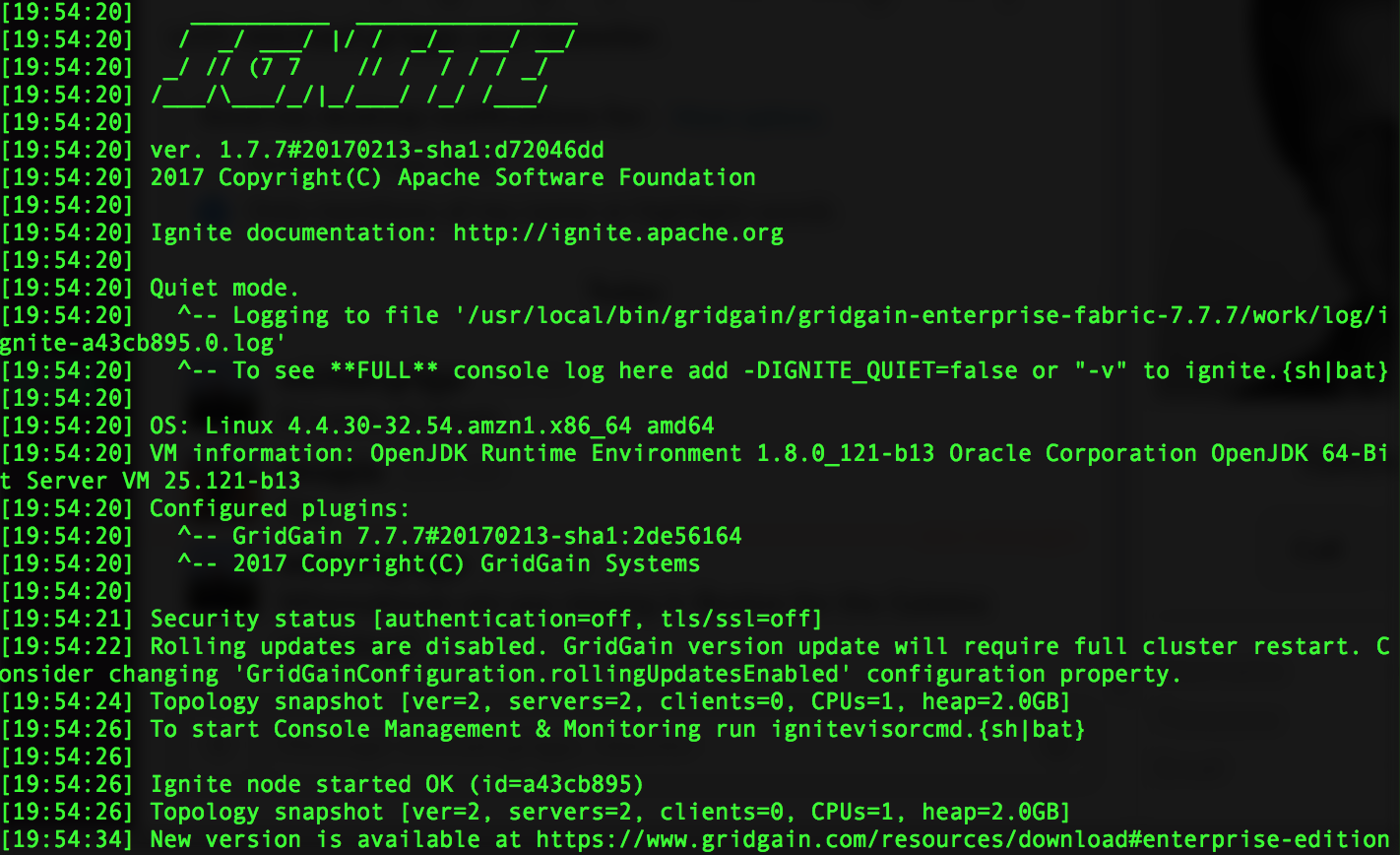
Looking at the logs of the second node we will note that "Topology snapshot" parameter reports there are already two GridGain server nodes joined a single cluster which is fully deployed on an EC2 AWS instance.
To be continued
It literally cost us five minutes to install and deploy the first GridGain cluster of two nodes on a single EC2 AWS instance. In the next blog post you'll discover how to accomplish the same across multiple EC2 instances and how to connect to the cluster from a developer environment in order to fill the cluster in with data and run various applications. Stay tuned!